Immune System, Weight Management
What Are The Symptoms Of B12 Deficiency?
Your bodies are remarkably adept at consuming, storing and using vitamins and minerals. But sometimes your entire diet and lifestyle can make it more strenuous to get sufficient of certain nutrients – which is where insufficiency comes in.
One of the vitamins which are most commonly associated with a lot of deficiencies in vitamin b12, which you require to maintain healthy blood and a healthy nervous system.
It is estimated by the National Health Service that B12 deficiency influence around 1 in 10 people aged 75 or over, and 1 in 20 people aged 65 to 74. The signs and symptoms of vitamin b12 deficiency can be physical or mental.
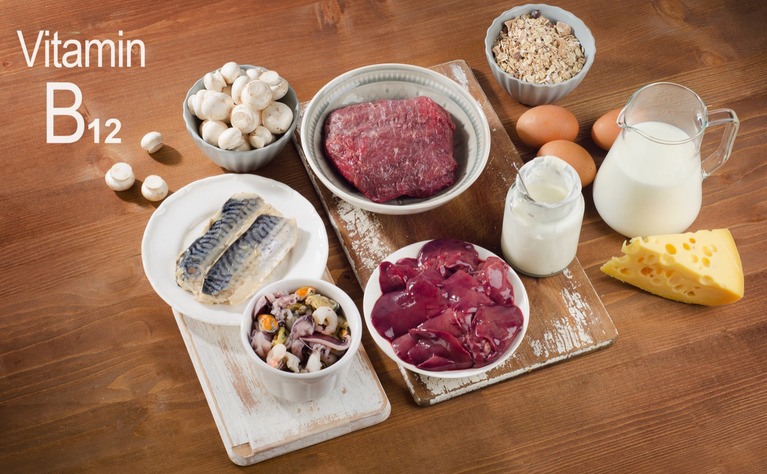 Vitamin b12 itself was determined during the investigation of pernicious anemia, a disease condition that damages epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete intrinsic element.
This intrinsic factor is required for vitamin b12 absorption.
If vitamin b12 levels are moderately lower than normal, it shows symptoms like fatigue, depression and also poor memory. It can also cause symptoms of mania (irritable mood) and psychosis.
Vitamin b12 deficiency majorly causes due to the insufficient dietary intake. It can also happen due to inappropriate absorption of vitamin b12. Therefore, those who consume high amounts of vitamin b12 may still experience deficiency.
Vitamin b12 deficiency occurs frequently among older people, caused primarily by “food-cobalamin malabsorption” (incapacity to release vitamin b12 from food or its binding proteins) and “pernicious anemia”.
The “Institute of medicine” suggested that 10 to 30% of older people may be unable to absorb vitamin b12 from a regular diet, it is advisable for those 51 years old and older to intake b12-fortified foods (adding vitamins and minerals to food) or b12 supplements to meet the daily requirements.
Vitamin b12 deficiency can be easily treated by long-term supplementation of vitamin b12. The recommended dietary intake of vitamin b12 for an adult is 2 to 3 µg per day.
Vitamin b12 itself was determined during the investigation of pernicious anemia, a disease condition that damages epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete intrinsic element.
This intrinsic factor is required for vitamin b12 absorption.
If vitamin b12 levels are moderately lower than normal, it shows symptoms like fatigue, depression and also poor memory. It can also cause symptoms of mania (irritable mood) and psychosis.
Vitamin b12 deficiency majorly causes due to the insufficient dietary intake. It can also happen due to inappropriate absorption of vitamin b12. Therefore, those who consume high amounts of vitamin b12 may still experience deficiency.
Vitamin b12 deficiency occurs frequently among older people, caused primarily by “food-cobalamin malabsorption” (incapacity to release vitamin b12 from food or its binding proteins) and “pernicious anemia”.
The “Institute of medicine” suggested that 10 to 30% of older people may be unable to absorb vitamin b12 from a regular diet, it is advisable for those 51 years old and older to intake b12-fortified foods (adding vitamins and minerals to food) or b12 supplements to meet the daily requirements.
Vitamin b12 deficiency can be easily treated by long-term supplementation of vitamin b12. The recommended dietary intake of vitamin b12 for an adult is 2 to 3 µg per day.
 Treatment includes raising your vitamin b12 levels and will vary based on the cause of your deficiency.
Your doctor may recommend:
Shots of vitamin b12 (monthly or more often, if needed)
Vitamin b12 supplements, in tablet form or as a nasal spray
Treatment of underlying conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or alcoholism.
Treatment includes raising your vitamin b12 levels and will vary based on the cause of your deficiency.
Your doctor may recommend:
Shots of vitamin b12 (monthly or more often, if needed)
Vitamin b12 supplements, in tablet form or as a nasal spray
Treatment of underlying conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or alcoholism.
What Are The Deficiencies Of Vitamin B12?
 Vitamin b12 itself was determined during the investigation of pernicious anemia, a disease condition that damages epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete intrinsic element.
This intrinsic factor is required for vitamin b12 absorption.
If vitamin b12 levels are moderately lower than normal, it shows symptoms like fatigue, depression and also poor memory. It can also cause symptoms of mania (irritable mood) and psychosis.
Vitamin b12 deficiency majorly causes due to the insufficient dietary intake. It can also happen due to inappropriate absorption of vitamin b12. Therefore, those who consume high amounts of vitamin b12 may still experience deficiency.
Vitamin b12 deficiency occurs frequently among older people, caused primarily by “food-cobalamin malabsorption” (incapacity to release vitamin b12 from food or its binding proteins) and “pernicious anemia”.
The “Institute of medicine” suggested that 10 to 30% of older people may be unable to absorb vitamin b12 from a regular diet, it is advisable for those 51 years old and older to intake b12-fortified foods (adding vitamins and minerals to food) or b12 supplements to meet the daily requirements.
Vitamin b12 deficiency can be easily treated by long-term supplementation of vitamin b12. The recommended dietary intake of vitamin b12 for an adult is 2 to 3 µg per day.
Vitamin b12 itself was determined during the investigation of pernicious anemia, a disease condition that damages epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete intrinsic element.
This intrinsic factor is required for vitamin b12 absorption.
If vitamin b12 levels are moderately lower than normal, it shows symptoms like fatigue, depression and also poor memory. It can also cause symptoms of mania (irritable mood) and psychosis.
Vitamin b12 deficiency majorly causes due to the insufficient dietary intake. It can also happen due to inappropriate absorption of vitamin b12. Therefore, those who consume high amounts of vitamin b12 may still experience deficiency.
Vitamin b12 deficiency occurs frequently among older people, caused primarily by “food-cobalamin malabsorption” (incapacity to release vitamin b12 from food or its binding proteins) and “pernicious anemia”.
The “Institute of medicine” suggested that 10 to 30% of older people may be unable to absorb vitamin b12 from a regular diet, it is advisable for those 51 years old and older to intake b12-fortified foods (adding vitamins and minerals to food) or b12 supplements to meet the daily requirements.
Vitamin b12 deficiency can be easily treated by long-term supplementation of vitamin b12. The recommended dietary intake of vitamin b12 for an adult is 2 to 3 µg per day.
What Are The Symptoms Of Vitamin B12 Deficiency?
Some don’t show any type of symptoms of a vitamin b12 deficiency, while others may experience:- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Tiredness
- Lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Swollen, red tongue
- Bleeding gums
- Loss of appetite
- Pale skin
- Lack of focus
- Depression
- Confusion
- Dementia
- Loss of balance
- Insensibility and tingling in your hands and also feet.
Treatment Of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
 Treatment includes raising your vitamin b12 levels and will vary based on the cause of your deficiency.
Your doctor may recommend:
Shots of vitamin b12 (monthly or more often, if needed)
Vitamin b12 supplements, in tablet form or as a nasal spray
Treatment of underlying conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or alcoholism.
Treatment includes raising your vitamin b12 levels and will vary based on the cause of your deficiency.
Your doctor may recommend:
Shots of vitamin b12 (monthly or more often, if needed)
Vitamin b12 supplements, in tablet form or as a nasal spray
Treatment of underlying conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or alcoholism.
Is Consuming High Doses of B12 Helpful Or Else Harmful?
Since b12 is a water-soluble vitamin, it’s usually considered safe, even at large doses. No tolerable upper intake level (UL) has been started for b12, due to its low level of toxicity. UL leads to the maximum daily dose of a vitamin unlikely to cause opposing side effects in the usual population. This threshold has not been set for vitamin b12 because your body excretes whatever it doesn’t use through your urine. However, supplementing with largely high levels of b12 has been linked to a few negative side effects. The number of studies has displayed that megadoses of the vitamin can lead to outbreaks of acne and also rosacea, a skin condition that causes redness and pus-filled bumps on your face. Yet, it should be noted that most of these researchers are focused on high-dose injections rather than the oral supplement. There is also some proof recommending that high doses of b12 may head to negative health outcomes in those with diabetes or kidney disorder. One research found that people with diabetic nephropathy (loss of kidney consequence due to diabetes) experienced a more rapid decrease in kidney function when supplemented with large-dose B vitamins, including 1 mg per day of b12. What’s more, the participants receiving the high-dose B vitamins had a higher risk of heart attack, stroke and death, compared to those receiving a placebo. Another research in pregnant women showed that extremely high b12 levels due to vitamin supplements enhanced the risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder in their offspring. Though there is proof that supplementing with b12 may cause negative health outcomes, researchers have demonstrated that daily oral supplements of up to 2 mg (2,000 mcg) are secure and effective in treating b12 deficiency. For reference, the suggested regular intake (RDI) of vitamin b12 is 2.4 mcg for both men and women, though pregnant women and breastfeeding women have a longer need.What Are The Vitamin B12 Side Effects?
- Restenosis (reoccurrence of narrowing of a blood vessel).
- Causes high blood pressure.
- Leads to acne.
- Rashes may appear.
- itchy or burning skin.
- pink or red skin discoloration.
- facial flushing.
- urine discoloration.
What Are The Age Wise Dosages?

- Infants up to 6 months old need 0.4 micrograms per day.
- The RDA for children between the ages of 1 and 3 years is 0.9 micrograms in a day, and for children from the years 4 to 8 the requirement is 1.2 micrograms per day.
- Children aged 9 to 13 years need 1.8 micrograms per day and everyone aged 14 and older require 2.4 micrograms per day.
- Vitamin b12 recommendations remain the same from teenage years throughout adulthood and into your golden years. You need 2.4 micrograms of vitamin b12 each day.
- Make sure a senior is taking 800-1000 IU per day or has been checked for a deficiency if there are any danger signs.


