Lifestyle, Stress Management
What Do You Know About Concussion?
Concussion- Causes and Symptoms
When you injure yourself, it is usually obvious. If you scrape your knee or if you break your arm, then obviously there will be bruising, bleeding, or swelling in order to show that some part of your body has been damaged already. A concussion is a traumatic brain injury. They are the result of a blow or jolt to the head which disrupts the normal function of your brain. Just like people, every other concussion is unique. In fact, the healthcare professionals in the field of brain injury denote this phrase – If you have seen one concussion, you have seen one concussion. The traumatic brain injury can have wide-ranging psychological as well as physical effects. Most of the signs or symptoms of a concussion are evident soon after the same traumatic event, while you may only become aware of the others days or weeks later.
What causes a concussion?

- A bump, blow, or jolt to the head, like a fall or collision which causes direct impact
- A blow or a fall to the body which causes the head to move quickly back and forth, although the head doesn’t suffer a direct hit, the brain is jostled inside the skull.
Whether or not a person has suffered a concussion isn’t always obvious. A loss of consciousness does happen in only about 10% of concussion cases. The standard neurological imaging, like MRIs and CT scans, are typically normal post concussions, however, are used to assess for more serious injuries.
Common signs
- Vomiting
- Irritability
- Drainage from their mouth, ears, or nose
- Drowsiness
At times, concussions can cause permanent brain damage. While most of the people recover from concussions, it is also important to have them checked out by a doctor. Always look for immediate medical help in this case.
Symptoms of Concussion
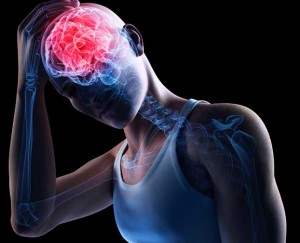
It ought to be noted that concussion doesn’t necessarily mean that you have to be unconscious for a specific period of time to be determined as having a concussion. There are plenty of symptoms that can give you a strong sign or warning regarding your concussion. Some of the symptoms are:
- Headaches or neck pain that does not go away
- Slowness in thinking, speaking, acting, or reading
- Difficulty remembering, concentrating, or making decisions
- Getting lost or easily confused
- Mood changes (feeling sad or angry for no reason)
- Feeling tired all of the time, having no energy or motivation
- Changes in sleep patterns (sleeping a lot more or having a hard time sleeping)
- Urge to vomit (nausea)
- Lightheadedness, dizziness, or loss of balance
- Increased sensitivity to lights, sounds, or distractions
- Loss of sense of smell or taste
- Ringing in the ears
- Blurred vision or eyes that tire easily
Most of the people make a good recovery from a concussion. However, it is important to take what may seem like just a bump on the head seriously. There is a common question, that is ‘when should I go to the hospital for if I doubt I have a concussion?’ The answer is, never delay! If you notice you or your loved one have any of the above symptoms, then you ought to seek medical attention right away. Although seemingly minor bumps can result in life-threatening brain bleeding or some other serious conditions which can only be identified as well as treated in a hospital.
What happens amid concussion?
The injury is dependent upon plenty of factors. However, it includes the amount of force and if the impact is rotational or linear. A metabolic cascade occurs within your brain which can last from minutes to hours. This is why it is critical to get proper treatment for concussion once you identify that, not to continue riding your bike, playing football, soccer, etc. on that same day. Also, the cascade of chemical changes which occur in the brain create a situation where the cerebral blood flow decreases and that results in the brain needing more energy than it is getting already. This leaves the brain vulnerable to a second ischemic injury.
How to prevent it?
Wearing protective gear during sports and other recreational activities
Ensure the equipment well-maintained, fits and worn correctly. Follow the rules of the game as well as practice good sportsmanship.
When motorcycling, bicycling, snowboarding or engaging in any other recreational activity which may result in head injury, wear a protective headgear.
Making your home safe
Always keep your home well-lit and your floors free of anything which might cause you to trip and fall. The falls around the home are a leading cause of most of the head injuries.
Buckling your seat belt

Wearing a seatbelt might prevent serious injury, including head injury, amid a traffic accident.
Protecting your children
In order to help lessen the risk of head injuries to your children, block off stairways and install window guards.
Educating others about concussions
Educating athletes, coaches, parents as well as others about concussions can help spread the awareness.
Exercising regularly

Regular exercise can strengthen your leg muscles as well as it can improve your balance.
Other complications
- Post-concussion syndrome – this causes you to experience concussion symptoms for weeks instead of just a few days
- Post-traumatic vertigo, or dizziness that lasts for up to several months
- Post-traumatic headaches, which may last for a few months
- Brain injuries from multiple TBIs
You can reduce your risk of getting a concussion just by wearing the correct helmet as well as other athletic safety gear during sports activities or other. Most of the people completely recover from their concussions, however, it may take months for the symptoms to disappear. In few instances, people experience mental, emotional, or physical changes which are more lasting. Also, repetitive concussions (ought to be avoided) although are rarely fatal, they can increase the chances of getting permanent brain damage.


